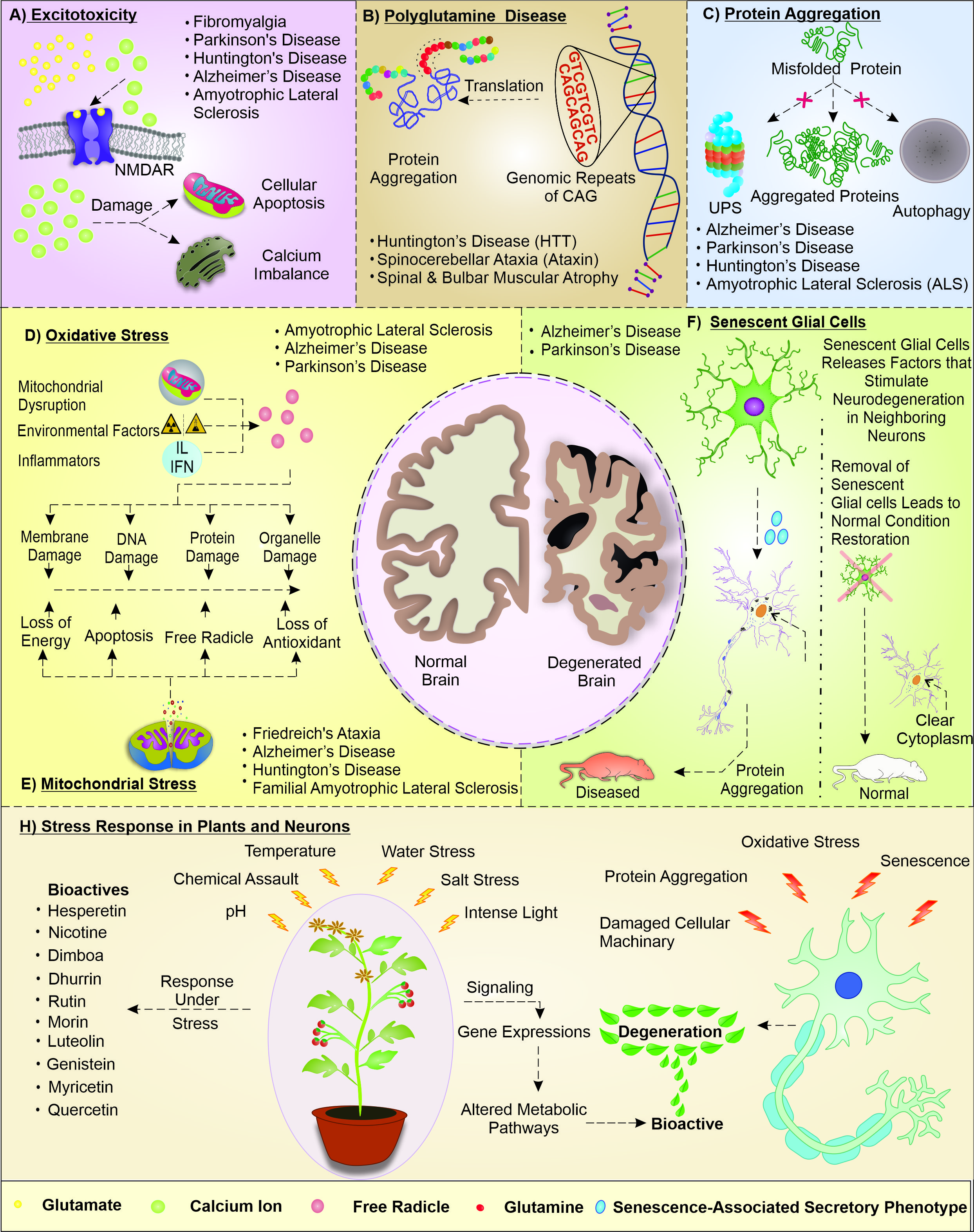
Fig. 1. The figure depicts the general disturbance in cellular and molecular mechanism of neuronal cells that lead to class of neurodegenerative disorders (NDD). (A) Increased calcium concentration inside the cell leads to serious damage to cellular machinery like Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) which would in turn increase the cellular calcium concentration and Mitochondria that would lead to disruption and consequently lead to apoptosis. (B) Occurrence of large stretch of CAG repeats in the genome (>40) lead to polyglutamine track in the protein which leads to destabilization of structure and result in misfolded protein that tend to form aggregated structures. (C) Overload for degradation of these molecular junk these is buildup of the misfolded proteins resulting into development of aggregates in the cytoplasm that forms the pathophysiology of various NDDs. (D) Free radicals lead to an array of malfunction in the cell leading to membrane damage, DNA damage, protein damage and organelle damage all of which lead to degeneration of neuron. (E) Mitochondrial stress could also lead to NDD by directly leading to apoptosis or depletion of energy for physiological activity of the neurons (F) This section shows the modulation of normal neuronal cell to a degenerative neuron by the neighboring senescent glial cells signaling that leads to manifestation of the diseased condition. (H) Plants are known to withhold various different stressful conditions by the production of various bioactive due to alterations in their normal biochemical pathways.